Please Note: This article is written for users of the following Microsoft Word versions: 97, 2000, 2002, and 2003. If you are using a later version (Word 2007 or later), this tip may not work for you. For a version of this tip written specifically for later versions of Word, click here: Understanding Sections.
Written by Allen Wyatt (last updated November 16, 2024)
This tip applies to Word 97, 2000, 2002, and 2003
If you have used Word for any length of time, you are aware that there are three general types of formatting you can use for a document: page formatting, paragraph formatting, and character formatting. In general, page formatting is set only once for an entire document. That is because your paper size seldom changes in the middle of a document. There are, however, other page formatting settings that you may want to change from time to time, even in the middle of a document. For instance, you may want to change the top margin on a particular page, or you may want to change the way that headers or footers appear on a particular page.
The way Word handles such mid-document page formatting changes is through the use of sections. A section is a portion of a document to which a certain set of page formatting properties should be applied. If you find yourself with the need to change anything having to do with page layout, simply create a new section and change the formatting for that section alone.
You insert a new section in your document by choosing Break from the Insert menu. Word displays the Break dialog box. (See Figure 1.)
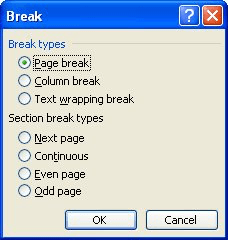
Figure 1. The Break dialog box.
You can select any of the following types of section breaks:
Select the type of section break you want and then click on OK. The section break is inserted, and you can format the new section (or old) as you desire. You can always tell which section you are in by looking at the status bar. Just to the left of the Page number is the notation Sec 1. This means you are in section 1 of your document. If the notation is Sec 3, you are in section 3. (You get the idea—you can have as many sections as you need in your document.)
WordTips is your source for cost-effective Microsoft Word training. (Microsoft Word is the most popular word processing software in the world.) This tip (1920) applies to Microsoft Word 97, 2000, 2002, and 2003. You can find a version of this tip for the ribbon interface of Word (Word 2007 and later) here: Understanding Sections.

Create Custom Apps with VBA! Discover how to extend the capabilities of Office 365 applications with VBA programming. Written in clear terms and understandable language, the book includes systematic tutorials and contains both intermediate and advanced content for experienced VB developers. Designed to be comprehensive, the book addresses not just one Office application, but the entire Office suite. Check out Mastering VBA for Microsoft Office 365 today!
Rather than have the margins of your documents always be the same, you can use what Word calls "mirror margins." Here's ...
Discover MoreSection breaks are used to divide a document into two or more sections that can be independently formatting. If you want ...
Discover MoreDocument backgrounds come in handy if you plan on converting the document to a Web page. Here's how you can add a ...
Discover MoreFREE SERVICE: Get tips like this every week in WordTips, a free productivity newsletter. Enter your address and click "Subscribe."
There are currently no comments for this tip. (Be the first to leave your comment—just use the simple form above!)
Got a version of Word that uses the menu interface (Word 97, Word 2000, Word 2002, or Word 2003)? This site is for you! If you use a later version of Word, visit our WordTips site focusing on the ribbon interface.
Visit the WordTips channel on YouTube
FREE SERVICE: Get tips like this every week in WordTips, a free productivity newsletter. Enter your address and click "Subscribe."
Copyright © 2026 Sharon Parq Associates, Inc.
Comments