Please Note: This article is written for users of the following Microsoft Word versions: 97, 2000, 2002, and 2003. If you are using a later version (Word 2007 or later), this tip may not work for you. For a version of this tip written specifically for later versions of Word, click here: Using Call to Run VBA Macros.
Written by Allen Wyatt (last updated August 11, 2018)
This tip applies to Word 97, 2000, 2002, and 2003
While it is possible to run a VBA macro from another macro by using the approach presented in the previous tip, there are times when such an approach just won't do the job. Instead, you need to look for a solution that allows a fail-safe method of running a macro. One approach is to use the Call command in VBA. Before you can use the command, however, you need to add a project reference to the calling project. (Projects are how VBA refers to the collection of VBA modules, forms, etc. in a template. For example, VBA refers to the Normal.dot template as the "Normal" project.) References between projects provide an unambiguous defined link between a calling project and the project to be called.
For instance, let's say that the MyMacro macro (the one you wanted to run) was a part of the CoolDoc template. To use Call properly in VBA, you need to add a reference to the CoolDoc.dot project to the macro that will call MyMacro. Unfortunately, this is a bit easier said than done because of a potential "gottcha" in VBA: Other than the "Normal" project, VBA gives all user-created template projects the default project name of "TemplateProject." This can create problems since having a unique project name is best when wishing be specific about the macro to run. To give CoolDoc.dot a unique project name, follow these steps:
If you expand all the objects under CoolDoc, you should see a module or two in the project. (Remember; VBA macros are contained in modules.) For the sake of this discussion, let's assume that MyMacro (the one you want to run) is contained within the HotStuff module of the CoolDoc project. (All these object names will be used shortly. At this point you just need to note the names used for your project and the module with the macro.)
Now you are ready to actually add the CoolDoc project reference to the project from which the macro will be called. In this instance, let's assume you will be calling it from a macro in the Normal project. You can add the reference by following these steps (assuming that the VBA editor is still open):
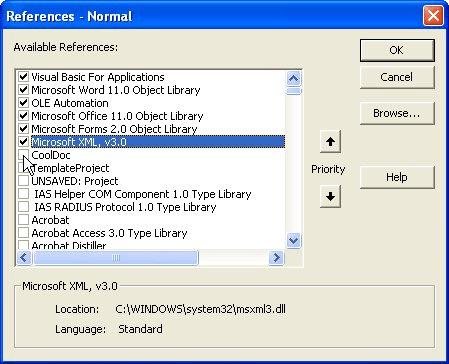
Figure 1. The References dialog box.
Finally you are ready to add the Call statement to the macro from which you want to call MyMacro. The command line would appear as follows:
Call CoolDoc.HotStuff.MyMacro
This command line causes VBA to run the desired macro, without any chance of ambiguity. There is something important to note, however. Putting a reference to the CoolDoc project in Normal makes Normal load a copy of CoolDoc every time Word is started—even if there are no documents open that are based on the CoolDoc.dot template.
This loading of CoolDoc raises and obvious question: What is the point, in VBA, of putting MyMacro in CoolDoc.dot since it won't save load time or resource usage? The short answer is that there isn't any point, other than CoolDoc.dot possibly being a more obvious place to put code that only relates to things in CoolDoc.dot. (This whole topic of sensible project design is far too big a subject to discuss in this single tip.)
Note:
WordTips is your source for cost-effective Microsoft Word training. (Microsoft Word is the most popular word processing software in the world.) This tip (86) applies to Microsoft Word 97, 2000, 2002, and 2003. You can find a version of this tip for the ribbon interface of Word (Word 2007 and later) here: Using Call to Run VBA Macros.

Learning Made Easy! Quickly teach yourself how to format, publish, and share your content using Word 2021 or Microsoft 365. With Step by Step, you set the pace, building and practicing the skills you need, just when you need them! Check out Microsoft Word Step by Step today!
Do some macro programming in VBA and you'll quickly find out that you can use functions to extend the power and ...
Discover MoreThe heart of creating powerful programs in VBA is to understand how to create subroutines. These structures allow you to ...
Discover MoreFunctions can be used to perform repetitive tasks and return values to your main program. You can also pass values to a ...
Discover MoreFREE SERVICE: Get tips like this every week in WordTips, a free productivity newsletter. Enter your address and click "Subscribe."
2019-06-18 16:23:00
Mendi
Excelent explanation !
Thank you much!
Mendi
Got a version of Word that uses the menu interface (Word 97, Word 2000, Word 2002, or Word 2003)? This site is for you! If you use a later version of Word, visit our WordTips site focusing on the ribbon interface.
Visit the WordTips channel on YouTube
FREE SERVICE: Get tips like this every week in WordTips, a free productivity newsletter. Enter your address and click "Subscribe."
Copyright © 2026 Sharon Parq Associates, Inc.
Comments